
A cold is one of the most common ailments in our daily lives. It is usually caused by a viral infection and presents with symptoms such as coughing, runny nose, sore throat, fever, and general discomfort. While Western medicine offers many effective treatments for colds, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) also provides unique therapeutic approaches.
Is cold and sick terrifying to you ? Click here to check on the other article that our practitioner analyze.
But is TCM suitable in treating cold ? This article explores this question from the perspective of TCM.
Understanding Colds in TCM
In TCM theory, a cold falls under the category of “external diseases,” mainly caused by the invasion of external pathogens (such as wind, cold, heat, and dampness) which impair the body’s vital energy, leading to a series of symptoms. Depending on the type of external pathogen, TCM categorizes colds into two main types:

1.Wind-Cold Cold:
Symptoms include aversion to cold, absence of sweating, headache, body aches, clear nasal discharge, and coughing with white phlegm. It commonly occurs when the temperature drops suddenly or during cold weather.

2.Wind-Heat Cold:
Symptoms include fever, mild aversion to wind, sweating, headache, sore throat, coughing with yellow phlegm, and yellow nasal discharge. It is common in hot weather or when the climate suddenly warms.
TCM Methods for Treating Colds
TCM treatments for colds primarily include herbal medicine, acupuncture, cupping therapy, and dietary therapy. Specific treatments are adjusted based on the type of cold and the individual’s constitution.
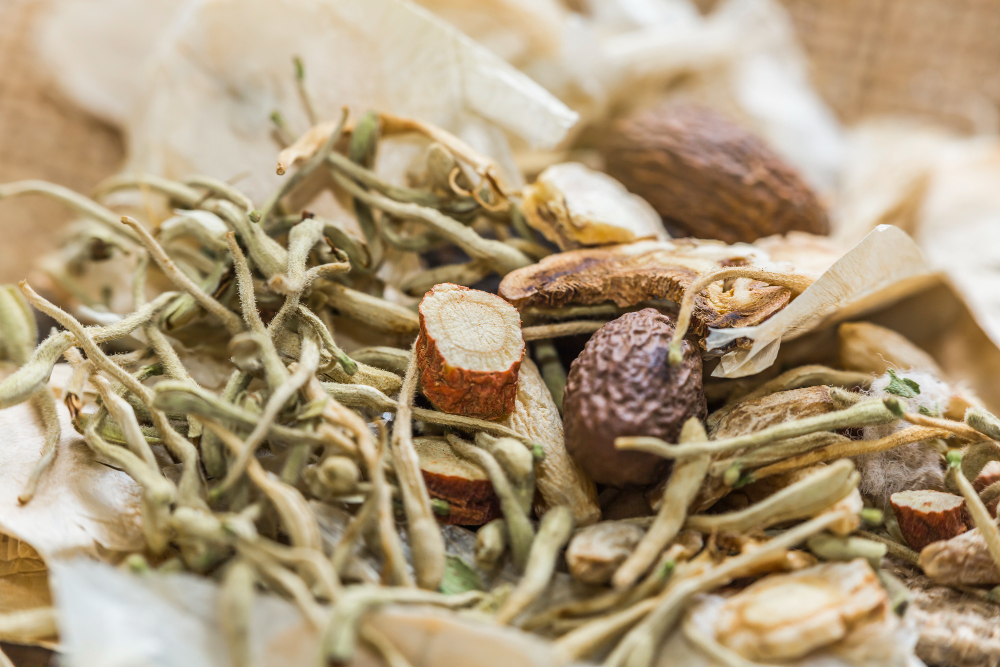

1.Herbal Medicine:
- Wind-Cold Cold: Common herbs include Schizonepeta (Jing Jie), Siler Root (Fang Feng), Perilla Leaf (Zi Su Ye), fresh ginger, and cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi), which have the effect of dispelling wind and cold.
- Wind-Heat Cold: Common herbs include Honeysuckle (Jin Yin Hua), Forsythia (Lian Qiao), Mulberry Leaf (Sang Ye), Chrysanthemum (Ju Hua), and peppermint, which have the effect of clearing heat and releasing the exterior.

2.Acupuncture:
Acupuncture stimulates specific acupoints to regulate the body’s qi and blood flow, enhancing immunity and alleviating cold symptoms. Common acupoints used are Hegu (LI4), Quchi (LI11), Fengchi (GB20), and Yingxiang (LI20).
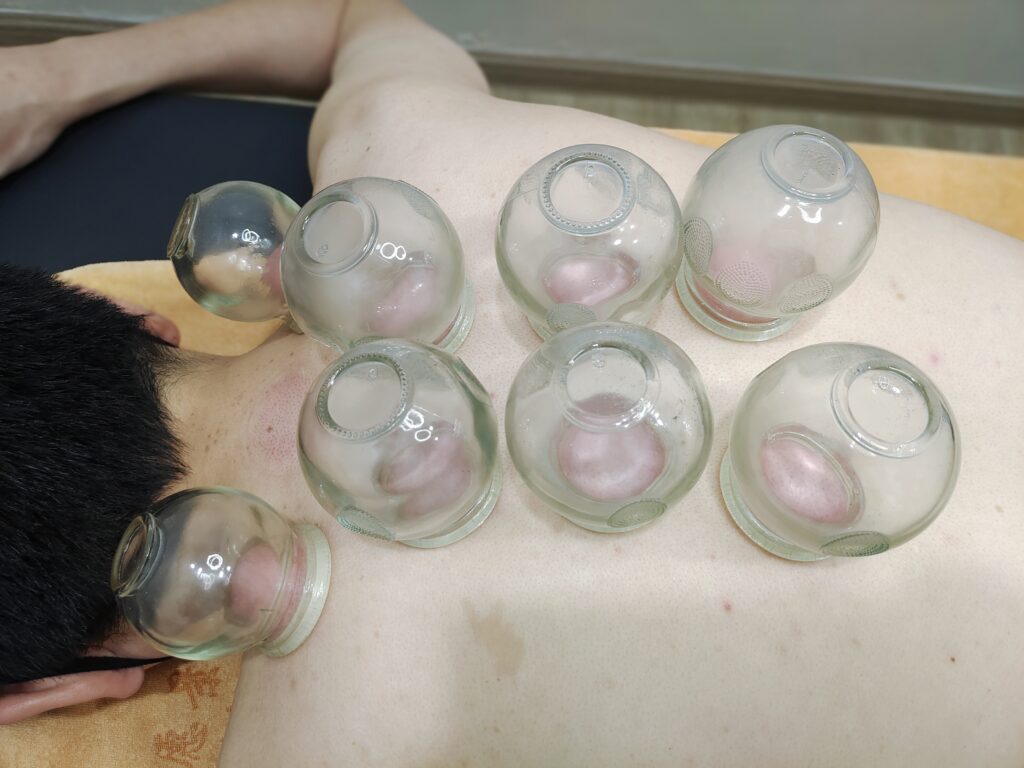
3.Cupping Therapy:
Cupping therapy creates suction on the skin to stimulate blood flow and metabolism, helping to expel internal cold and dampness, thus relieving cold symptoms.
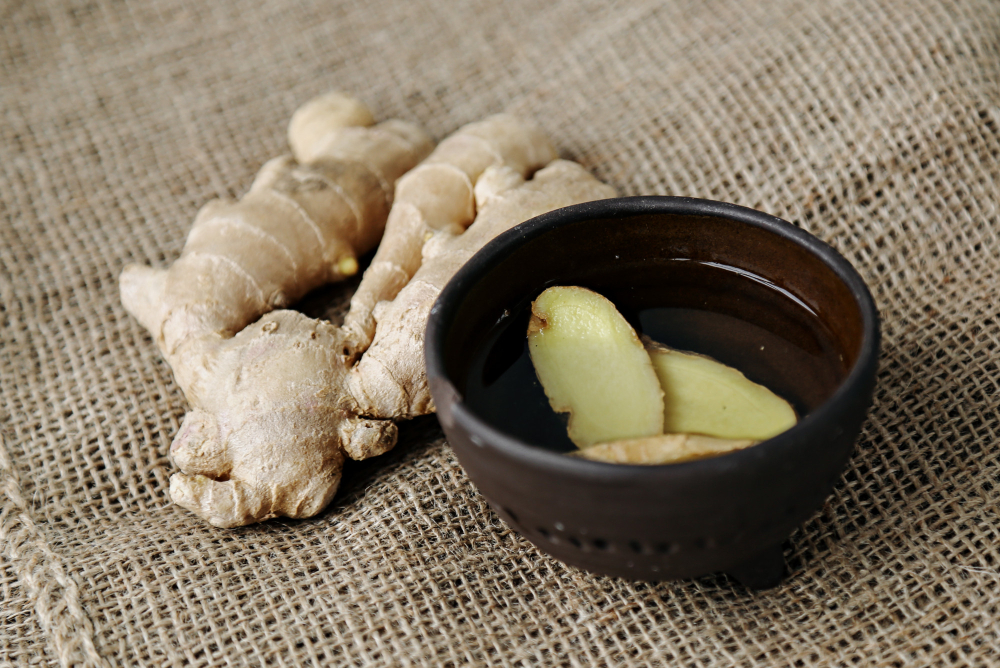

3.Dietary Therapy:
TCM advocates for dietary adjustments to nurture the body and prevent colds. Common dietary remedies include ginger tea (fresh ginger, red dates, and brown sugar), scallion soup (scallion and fresh ginger), and white fungus soup.

Advantages of TCM in Treating Colds
1.Individualized Treatment:
TCM emphasizes syndrome differentiation and treatment, offering personalized therapy based on the patient’s specific condition, thus improving efficacy.
2.Holistic Regulation:
TCM not only focuses on symptom relief but also on overall regulation, enhancing the patient’s constitution and preventing recurrence of colds.
3.Fewer Side Effects:
TCM herbs are mostly natural, and combined with therapies like acupuncture, they have fewer side effects, making them suitable for long-term management and treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, TCM is suitable in treating cold.Through syndrome differentiation and the combination of herbal medicine, acupuncture, cupping therapy, and dietary therapy, TCM can effectively alleviate cold symptoms, enhance immunity, and prevent recurrence.
Ultimately, whether choosing TCM or Western medicine, maintaining good lifestyle habits, adequate rest, and proper nutrition are key to preventing and treating colds.
此文章还有以下语言版本:
![]() 简体中文 (Chinese (Simplified))
简体中文 (Chinese (Simplified))



